Table of Contents
Introduction
Email is still one of the highest-ROI channels you own — and with ChatGPT-5 it becomes dramatically faster and smarter to create emails that actually convert. In the sections below I’ll walk you through a practical, marketer-first system for using ChatGPT-5 to plan, write, and measure high-conversion campaigns while keeping your brand voice, data privacy, and deliverability intact.
Why ChatGPT-5 changes the email marketing playbook (brief framing)
ChatGPT-5 isn’t just a faster copy machine — it’s a flexible creative partner that can generate tailored language, testable variants, and iterative improvements at scale. Instead of drafting one static email and hoping it lands, you can programmatically produce dozens of subject lines, preview texts, and body variations tuned to different segments and behaviors. That means more relevant messages, more experimentation, and a steeper learning curve for your funnels — provided you pair the model with good data, strong prompts, and human review.
What this guide covers and how to use the outline
This guide focuses on the practical steps you need to build high-conversion email campaigns powered by ChatGPT-5. We start with strategy and goals, move into data and segmentation, then cover backend setup (data hygiene and integrations), show how to engineer prompts that produce repeatable results, and finish with concrete copywriting frameworks and microcopy tips. Use this as a step-by-step checklist: read the strategy sections to set direction, use the prompt and copy sections when drafting, and apply the data and QA advice before you send.
1. Strategy & Goals
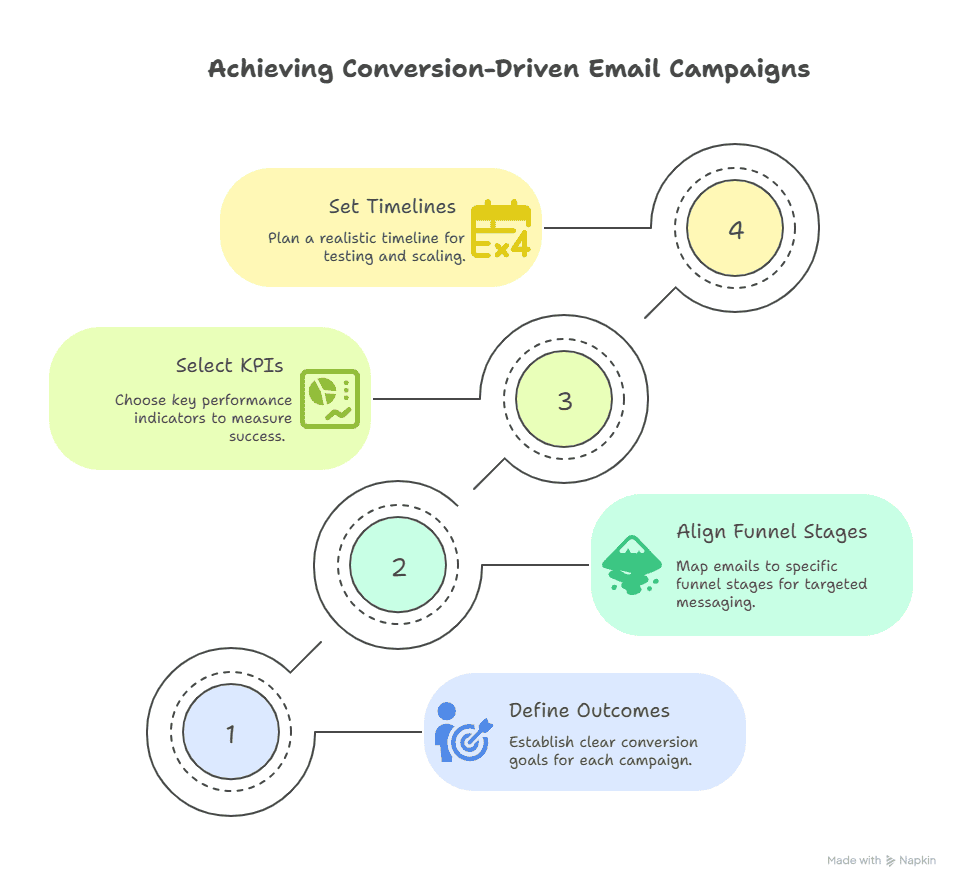
A conversion-driven campaign begins with clarity: what exactly should the email accomplish, and how will you measure success? Define those first, then let copy, segmentation, and testing decisions flow from them.
1.1 Define conversion outcomes (sales, signups, retention, referrals)
Be explicit about the primary conversion for each campaign. Is the goal a direct purchase, a free-trial signup, a webinar registration, or reactivation of dormant users? Each outcome requires different language and urgency. For example: sales require clear product benefits and frictionless CTAs; retention often needs value reminders and loyalty incentives; referrals should highlight an easy sharing mechanism and the reward structure.
1.2 Align email goals with funnel stages (TOFU, MOFU, BOFU)
Map every email to the funnel stage it’s meant to progress. Top-of-funnel (TOFU) emails educate and build trust with light asks; middle-of-funnel (MOFU) messages nurture with demos, case studies, or product comparisons; bottom-of-funnel (BOFU) communications push for conversion with strong social proof, scarcity, or discounts. ChatGPT-5 can switch tone and structure quickly once you declare the funnel role in your prompt.
1.3 KPI selection and success criteria (CTR, CVR, revenue per recipient)
Choose 3–5 KPIs that reflect the campaign’s objective and are actionable. Common choices:
- Open Rate and Subject Line CTR (subject line and sender tests)
- Click-Through Rate (CTR) — measures engagement with your offer
- Conversion Rate (CVR) — the single most meaningful metric for revenue-focused emails
- Revenue per Recipient or Revenue per Click — ties email performance directly to business outcomes
Set numeric targets (e.g., lift CTR by 15% vs. baseline) so your tests have clear success thresholds.
1.4 Setting realistic timelines and cohort targets
Define a realistic timeline for learning and scale. For a new campaign, plan a 4–12 week pilot: week 1–2 for data and templates, weeks 3–6 for A/B tests and signal collection, weeks 7–12 for scaling winning variants. Pick cohort sizes large enough to reach significance for your main metric (CTR or CVR) and segment tests so results aren’t diluted by mixed audiences.
2. Audience Intelligence (Segmentation & Data)
Personalization only works when it’s relevant. Good segmentation, powered by first-party data, lets you use ChatGPT-5 to craft messages that truly resonate.
2.1 Collecting the right first-party signals (behavioral, transactional, profile)
Prioritize data that predicts intent: page views, product categories browsed, cart additions, last purchase date, email engagement, and transaction history. Profile fields like industry, company size, or role are useful for B2B. Behavioral triggers (e.g., abandoned cart at checkout) are gold for timely, high-intent emails.
2.2 Designing mutually exclusive segments (new subscribers, active buyers, dormant)
Create clear, non-overlapping segments so messaging can be precise. Examples:
- New subscribers: signed up in last 7 days, no purchases
- Active buyers: purchased in last 90 days
- Dormant: last purchase >12 months or no opens in 90 days
Mutually exclusive segments avoid sending conflicting offers and make it simpler to test which message type moves each group.
2.3 Persona building with ChatGPT-5 (job-to-be-done prompts & outputs)
Use ChatGPT-5 to enrich personas: feed the model a compact profile — demographics + behavior + pain points — and ask for a 3-line persona summary, their top objections, and a suggested messaging angle. Prompts framed as “Act as an email strategist for [persona]; produce 3 pain-based hooks and 2 subject lines” yield targeted copy that maps to real user jobs.
2.4 Enrichment and psychographic layering (surveys, preference centers)
Augment behavior with voluntary inputs: quick preference centers, micro-surveys, and post-purchase feedback. These signals help ChatGPT-5 tailor tone and offers (e.g., price-sensitive vs. feature-driven). Offer incentives for preferences (e.g., “pick topics you care about — get 10% off”) to improve data quality.
3. Data Hygiene & Infrastructure
A model is only as good as the data you feed it. Clean, well-structured data plus the right integrations make personalization safe and scalable.
3.1 Required data model for personalization (fields, event logs)
Standardize a minimal data model your scripts and prompts can rely on:
- Profile: email, first_name, signup_date, locale, timezone
- Transactional: last_purchase_date, lifetime_value, avg_order_value
- Behavioral events: last_open_date, last_click_date, product_viewed, cart_abandon_event
- Flags: unsubscribed, spam_complaint, suppression_reason
Maintain these in a central source (CDP or CRM) to avoid mismatches.
3.2 Cleaning, deduping, and normalization processes
Automate dedupe and normalization workflows: canonicalize emails, normalize country and timezone codes, and resolve identity via deterministic keys (email) or probabilistic matching when needed. Regularly remove stale or invalid addresses and implement suppression lists for hard bounces and complaints.
3.3 Integrations: ESP, CRM, analytics, CDP — what you must connect
Your stack should connect at minimum: ESP for sending, CRM for customer records, analytics for attribution, and a CDP or data layer to unify events. Webhooks and API connections allow ChatGPT-5 generated content to be injected into templates or workflows programmatically while preserving personalization tokens.
3.4 Privacy-compliant storage and consent tracking
Track consent and preferences in a way that’s queryable by campaigns. Store only what you need for personalization and avoid embedding raw PII into prompts. Implement an audit trail for data usage and a clear process to honor deletion requests.
4. Prompt Engineering for Email Strategy
Prompting is where strategy meets execution. Well-designed prompts make ChatGPT-5 produce predictable, usable email drafts every time.
4.1 Core prompt patterns for strategy ideation (brief + constraints)
Start with a brief that states role, audience, goal, constraints, and format. Example pattern:
“Act as a senior email marketer. Audience: [segment]. Goal: [conversion outcome]. Constraints: [word count, tone, include CTA, product facts]. Output: subject lines (5), preview text (3), body copy (3 variants, 80–120 words).”
This clear scaffolding reduces trial-and-error and keeps outputs aligned to your KPI.
4.2 Building reproducible prompt templates (input schema + expected output)
Define an input schema your team or automation can populate: {first_name, segment, product_name, discount, urgency_flag, testimonial}. Create a template prompt that references each field explicitly, and define the exact output structure (e.g., JSON with keys subject, preview, body). Reproducibility matters when you scale.
4.3 Prompt chaining to refine subject lines, previews, and body copy
Use prompt chaining: generate many subject lines, then feed top performers into a second prompt that optimizes for tone, length, or emoji usage. Similarly, create preview text variants that complement chosen subjects — chaining lets you orchestrate multi-part outputs that interlock instead of clash.
4.4 Guardrails: instruction tokens, temperature, sampling for consistent tone
Set guardrails to maintain brand safety: specify tone (“friendly, professional”), banned phrases, and factual constraints. For consistent results, keep temperature low for factual outputs (0.2–0.4) and raise it slightly (0.4–0.7) when you want creative subject lines. Use top_p or nucleus sampling sparingly to control diversity and ensure repeatability.
5. Copywriting Frameworks with ChatGPT-5
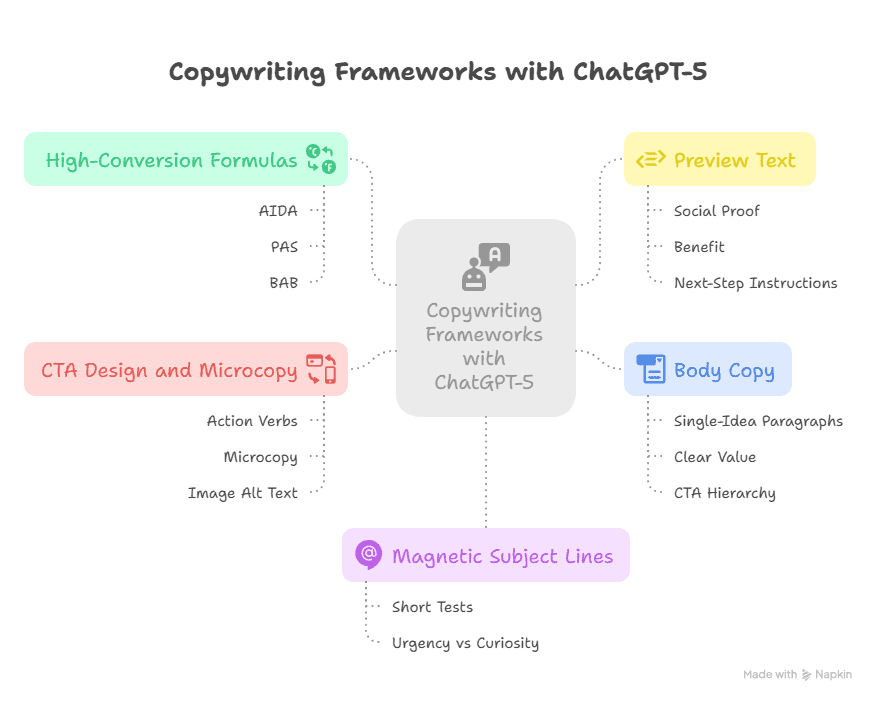
Marry classic persuasion formulas with AI prompts to produce repeatable, high-converting copy that reads human.
5.1 High-conversion formulas (AIDA, PAS, BAB) mapped to prompts
Map frameworks to templates:
- AIDA: Attention (subject), Interest (first line), Desire (benefits), Action (CTA). Prompt the model: “Write an AIDA email for [audience] selling .”
- PAS: Problem, Agitate, Solve — great for pain-driven offers.
- BAB: Before, After, Bridge — effective for illustrating transformation.
Ask ChatGPT-5 to label sections accordingly so editors can quickly see structure.
5.2 Writing magnetic subject lines (short tests + urgency vs curiosity)
Create at least 8–12 subject lines per send and test them. Keep core rules: 30–60 characters for mobile clarity, use personalization tokens sparingly, and align promise with the email body to avoid disappointments. Use urgency when it’s real (limited stock, deadline) and curiosity when you can deliver on the intrigue within the message. Always A/B test extremes (direct offer vs curiosity hook) to learn what your audience prefers.
5.3 Preview text that complements the subject line
Preview text should extend the promise of the subject, not repeat it. Use it to add social proof (“Loved by 10,000+ founders”), a short benefit, or next-step instructions. Aim for 35–90 characters visible on most clients. When using ChatGPT-5, ask for 3 preview variations ranked by “clarity,” “urgency,” and “curiosity.”
5.4 Body copy: single-idea paragraphs, clear value, call to action hierarchy
Write short, single-idea paragraphs and use bullets for fast scanning. Lead with the benefit, then add one piece of proof (stat, testimonial, or feature) and end with a primary CTA. If you need a secondary CTA (learn more, view demo), make it visually weaker. In prompts, require the model to keep paragraphs <= 2 sentences and include a one-line social proof element to boost credibility.
5.5 CTA design and microcopy (buttons, links, image alt text)
CTAs should use action verbs and set expectations: “Get 20% off now,” “Start your free trial — 2 minutes.” For buttons, keep microcopy tight (2–4 words) and use supporting link text for secondary actions. Don’t forget image alt text — prompt ChatGPT-5 to generate concise alt text for hero images that communicates the core benefit for accessibility and deliverability.
Sections 6–10: Personalization, Design, Automation, Testing & Deliverability
6. Personalization Strategies (Dynamic Content)
Personalization is the difference between a generic blast and a message that feels hand-crafted for the reader. With the right data model and a measured use of dynamic content, you can make readers feel seen without crossing privacy or relevance lines.
6.1 1:1 personalization vs. dynamic blocks — when to use each
1:1 personalization injects truly unique details into each email (first-name, last purchase, recommended product based on browsing). Use 1:1 when you have strong, recent signals and the action is high-stakes (cart recovery, renewal reminders, transactional receipts). Dynamic blocks serve groups of people with different content blocks inside the same template (e.g., “if in segment A show block A, else show block B”). Use blocks when you need scale and the differences are categorical (new vs returning customers, region-based promos). In short: 1:1 = intimacy + precision (higher development cost); dynamic blocks = efficiency + maintainability (easier to test and scale).
6.2 Behavioral triggers (cart abandonment, browse abandonment, milestone)
Behavioral triggers are time-sensitive and yield high intent. Common triggers:
- Cart abandonment: send within 1–6 hours with product image, price, and one-click recovery CTA.
- Browse abandonment: target users who viewed product pages but didn’t add to cart — highlight benefits and similar items.
- Milestones: birthdays, anniversaries, subscription renewals — use to deepen loyalty with relevance-driven offers.
Design triggers to run on event thresholds (e.g., cart abandoned and no purchase within 2 hours) and include suppression rules so you don’t send redundant messages.
6.3 Using ChatGPT-5 to generate dynamic snippets per segment
Treat ChatGPT-5 as a content factory for small, high-impact snippets: hero lines, micro-CTAs, product descriptions, social-proof snippets. Feed the model a compact schema (segment, product, recent action, tone) and request output in JSON: {subject, preview, snippetA, snippetB, alt_text}. Keep snippets short and test them as interchangeable “content atoms” that can be stitched into templates by your ESP. Important safety note: never place raw PII into prompts; use IDs or hashed references and fetch personal details server-side when rendering final templates.
6.4 Localization and cultural adaptation workflows
Localization goes beyond translation. For each locale:
- Swap currency, date formats, and timezone-aware send windows.
- Adapt imagery, idioms, and offer types to local tastes (e.g., free shipping thresholds vs discount percentages).
- Use translation memory and glossaries to keep brand voice consistent, then have native reviewers validate nuance and compliance.
Automate the initial translation and cultural adaptation with ChatGPT-5, then route results for human QA before launch.
7. Design, Layout & Accessibility
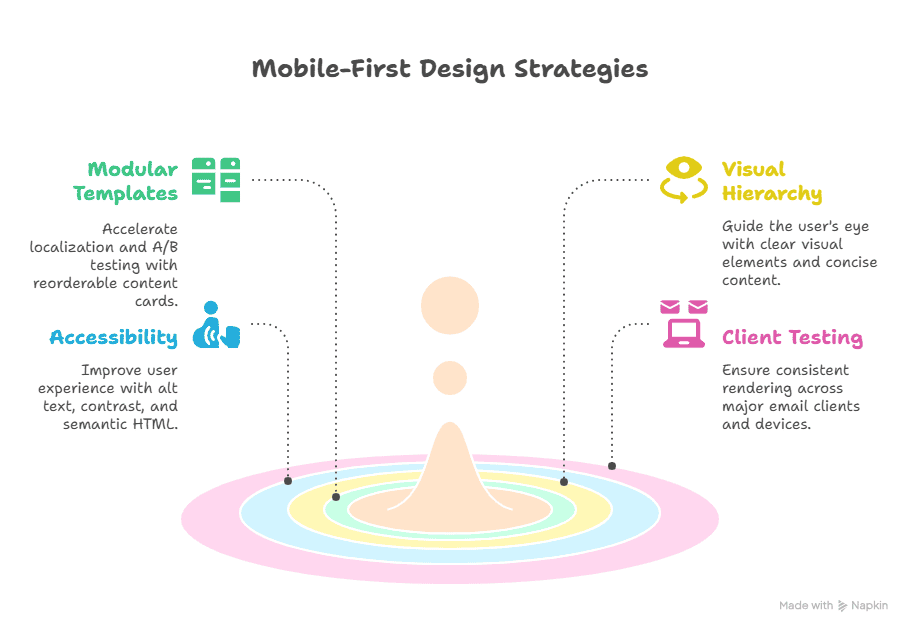
A great copy needs a clean, accessible stage. Design choices affect readability, conversion, and deliverability — especially on mobile.
7.1 Mobile-first modular templates (single-column flow)
Build single-column templates that stack cleanly on small screens. Use modular “content cards” (preheader → hero → body → social proof → CTA → footer) so pieces can be reordered per campaign without rebuilding templates. Modular templates accelerate localization, A/B tests, and dynamic block swaps.
7.2 Visual hierarchy: preheader, hero, body, social proof, CTA
Visual hierarchy guides the eye:
- Preheader: short extension of subject line — sets expectation.
- Hero: single, clear value proposition or image with concise headline.
- Body: 1–3 short paragraphs or bullets that support the hero.
- Social proof: testimonial, rating, or number of users to reduce friction.
- CTA: single primary action visually prominent; any secondary actions are low-contrast links. Keep line length short and use whitespace generously to increase scanability.
7.3 Accessibility: alt text, read order, contrast, semantic HTML
Accessibility improves user experience for everyone and reduces risks of content being misunderstood by screen readers:
- Alt text: describe the image’s function succinctly (not decorative).
- Read order: code structure must match visual order for screen readers.
- Contrast: ensure text and CTAs meet contrast ratios for legibility.
- Semantic HTML & ARIA: use proper tags so assistive tech can parse the content. Also avoid embedding critical info in images only — always include textual copies of core messages.
7.4 Testing rendering across major clients (Gmail, Outlook, Apple Mail)
Clients render HTML differently—test early and often. Check:
- Gmail/Android: responsive CSS quirks and web fonts fallbacks.
- Outlook: table-based fallbacks and limited CSS support.
- Apple Mail/iOS: image scaling and dark-mode behavior.
Also test with images blocked, dark mode enabled, and on different screen widths. Use a sampling of real devices and, when possible, inbox testing platforms to catch edge cases.
8. Automation & Orchestration
Automation turns one-offs into scalable journeys. Good orchestration maps customer states and governs how and when messages fire.
8.1 Journey maps: welcome, activation, nurture, re-engagement
Sketch journeys around outcomes:
- Welcome series: orient, deliver promised value, and request a small action.
- Activation: nudges to complete a setup or first use.
- Nurture: education and progressive profiling to move prospects down-funnel.
- Re-engagement: progressive win-back offers with diminishing frequency and escalating value.
Design KPIs and decision points for each node so the flow adapts to user behavior (e.g., skip steps for users who take the action early).
8.2 Trigger rules and throttling (rate limits, suppression lists)
Trigger rules define when events create sends; throttling protects the user experience:
- Rate limits: cap emails per user per day/week to avoid fatigue.
- Suppression lists: global unsubscribe, bounce, and complaint lists must always override triggers.
- Priority rules: transactional > lifecycle > promotional to ensure critical messages get through.
These safeguards protect deliverability and customer relationships.
8.3 Using ChatGPT-5 inside automation: auto-draft + human-in-loop approval
A practical workflow:
- Automation fires and gathers contextual data.
- ChatGPT-5 produces 3–5 draft variants (subject + preview + body snippet).
- Drafts are stored in the ESP as draft templates or sent to a review queue.
- Human editor selects, tweaks, and approves for send.
This preserves speed while keeping brand safety and compliance in the human loop. Tag drafts with metadata (reason for send, segment, timestamp) for auditability.
8.4 Scaling flows with template variables and localization pipelines
Use template variables ({{first_name}}, {{product_name}}, {{discount_pct}}) and centralize content packs for each locale. Implement a pipeline where:
- Content is generated once, localized, QA’d, and stored in a translation/content repository.
- Flows reference content IDs rather than fixed strings.
This reduces duplication, simplifies updates, and accelerates multi-market rollouts.
9. A/B and Multivariate Testing
Testing is how you turn assumptions into learning. Start simple, iterate fast, and avoid testing too many variables at once.
9.1 What to test first (subject, preview, CTA, sender name)
Prioritize by impact and ease:
- Subject line and sender name — highest open impact.
- Preview text — influences open decisions and complements subject lines.
- Primary CTA and hero messaging — drives click and conversion.
Run one major test at a time within a flow to get clear signals before moving to smaller micro-tests.
9.2 Statistical significance and sample-size calculation
Decide on the minimum detectable effect you care about (e.g., 10% lift in CTR) and calculate sample sizes accordingly. Small lists require larger relative lifts to detect significance; large lists can detect smaller lifts. Use standard sample-size calculators and set a confidence level (commonly 95%). Beware of peeking—stop-testing rules prevent false positives.
9.3 Automated testing prompts for ChatGPT-5 to generate test variants
Create prompt templates that instruct ChatGPT-5 to produce controlled variants. Example:
“Generate 6 subject lines for [segment] about [offer]. Keep 3 direct-promise, 3 curiosity hooks; max 45 characters each.”
For body tests, ask for variants that change only the CTA or opening sentence so the test isolates the variable. Keep an audit trail of which prompt produced which variant so you can iterate on the prompt itself.
9.4 Interpreting results and iterating quickly
Don’t just look at the winning subject line — examine downstream metrics (CTR, CVR, revenue per recipient). A subject that drives opens but low conversions might be misleading or misaligned with the email body. If a test is inconclusive, increase sample size or run a follow-up test that isolates a smaller variable. Document learnings in a test library to guide future hypothesis design.
10. Deliverability & Sender Reputation
Even the best copy fails if it never reaches the inbox. Protecting deliverability is a continuous, multi-layered effort.
10.1 Authentication essentials (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Authenticate your sending domain to prove mail legitimacy:
- SPF authorizes sending IPs for your domain.
- DKIM signs messages so recipients can verify content integrity.
- DMARC creates policy and reporting rules to handle spoofing.
Work with your DNS and ESP to ensure these records are properly configured and monitored.
10.2 List quality, sending cadence, and warmup best practices
Healthy lists are engaged lists. Best practices:
- Remove persistent non-openers or put them into re-engagement streams.
- Gradually warm new IPs and domains—start small and increase volume while monitoring complaint rates.
- Optimize cadence to your audience: test frequency, but err on the side of predictability rather than surprise.
10.3 Monitoring deliverability signals (bounce, spam complaints, engagement)
Key signals to watch:
- Hard bounces: remove immediately.
- Soft bounces: monitor; temporary issues may resolve.
- Spam complaints: investigate content and list source; suppress complainers immediately.
- Engagement metrics: sustained drops in opens/clicks often precede deliverability problems. Use ESP dashboards and DMARC reports to collect telemetry.
10.4 Remediation playbook for deliverability issues
When problems surface:
- Pause high-volume sends to the affected segment.
- Audit recent content and subject lines for spammy patterns or aggressive language.
- Check authentication (SPF/DKIM/DMARC) and sending IP reputation.
- Rehydrate a smaller, highly engaged subset to re-establish positive engagement signals.
- Clean the list (remove stale addresses) and review acquisition sources.
Document steps and thresholds so the team can act quickly next time.
11. Measurement & Analytics
Measurement is where opinions become decisions. Build your analytics so every send tells you not just what happened, but why — and what to try next.
11.1 Core metrics vs. vanity metrics (opens, clicks, conversions, LTV)
Separate the signal from the noise. Vanity metrics (opens, raw subscriber count) feel good but don’t always tie to business outcomes. Core metrics you should prioritize: Click-Through Rate (CTR) — shows interest in the message; Conversion Rate (CVR) — directly ties email activity to the desired action; Revenue per Recipient (RPR) or Revenue per Click — ties to monetary impact; and Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) — shows long-term value generated by email cohorts. Use opens to evaluate subject-line experiments and deliverability issues, but always layer downstream metrics (clicks → conversions → revenue) to judge true lift.
11.2 Setting up attribution: UTM strategy and event tracking
Give every link a predictable UTM pattern so analytics and ad platforms attribute traffic and conversions cleanly. Use a consistent schema: utm_source=email, utm_medium=email, utm_campaign=yyyymm_offername, utm_content=variantA (for A/B tests). Complement UTMs with deterministic event tracking (e.g., email_click, checkout_started, purchase_completed) that includes campaign_id and user_id so you can stitch sessions to users in your analytics or CDP. Track the same event names across channels for easy funnel comparisons. Finally, ensure server-side events and client-side analytics align — mismatches are the most common cause of attribution confusion.
11.3 Dashboards and reports to measure funnel lift
Create dashboards that tell a story at a glance: Top-level funnel (sends → opens → clicks → conversions → revenue) plus segmented views by cohort, campaign, and channel. Include cohort analysis (e.g., users acquired via welcome series vs. paid), time-to-conversion curves, and A/B test result panels with confidence intervals. Build alerts for KPI drifts (drop in CTR > X% week-over-week) and a “test library” dashboard showing past hypothesis, sample size, results, and learnings — this turns ad-hoc wins into repeatable playbooks.
11.4 Using ChatGPT-5 to summarize performance and recommend actions
Feed aggregated, non-PII performance summaries to ChatGPT-5 and ask for structured insights: “Summarize last 30 days: CTR, CVR, revenue per recipient by campaign; highlight top 3 underperformers and suggest 4 action items.” Use the model to translate raw numbers into hypotheses (e.g., “high opens, low clicks — subject promise mismatch”) and prioritized experiments. Keep guardrails: send only aggregated metrics (no raw PII), include baselines, and request explicit next steps with testable hypotheses. Always have a human validate recommendations before execution.
12. Legal & Compliance
Good personalization and aggressive optimization must live inside the law and ethical practice. Compliance protects customers and your sender reputation.
12.1 Consent, CAN-SPAM, GDPR basics for email copy and data use
Follow the highest standard that applies to your audience. Key points:
- CAN-SPAM (US): include a valid physical address, clear opt-out link, and honour opt-outs promptly.
- GDPR (EU): require lawful basis (consent or legitimate interest) for marketing; consent must be explicit, documented, and revocable; process data minimization and DPIA where required.
- Store proof of consent (timestamps, source) and make it easy for users to update preferences. Align copy and opt-in flows to avoid misleading promises.
12.2 Required footer and opt-out language templates
Keep footers concise and compliant. A minimal template:
You’re receiving this email because you signed up at [yourdomain.com]. Our mailing address: [Company Legal Address]. Manage your preferences or unsubscribe here: [unsubscribe_link].
For GDPR audiences include: “You can withdraw consent or request data removal at any time by contacting [[email protected]].”
12.3 Security considerations when using LLMs (PII & prompt exposure)
Never pass raw PII (full email addresses, payment data, national IDs, health details) into public or shared LLM prompts. Techniques to reduce risk:
- Tokenize or hash identifiers in prompts and fetch personal data server-side when rendering final templates.
- Use internal, enterprise LLM deployments or vetted APIs with contractual data handling guarantees.
- Redact or anonymize examples used for prompt tuning.
- Limit who can issue production prompts and log prompt usage for audits.
12.4 Audit logs, versioning, and retention policies
Track everything: who generated what prompt, which model was used, output ID, approval states, and send timestamps. Version both prompts and template content so you can rollback if a copy causes issues (legal, brand, or performance). Define retention windows for logs and message content that meet local regulations, and ensure deletion requests are actionable across backups and archives.
13. Creative Tactics & High-Impact Use Cases
Beyond the fundamentals, creative execution drives standout performance. These tactics are high-leverage when done thoughtfully.
13.1 Conversational emails that mimic 1:1 outreach
Write short, context-rich messages that feel personal: a single sentence opener referencing a recent action, a concise value proposition, and a direct ask. Use ChatGPT-5 to craft multiple “micro-variants” of a conversational opener that include subtle personalization (recent product, location-based note, or usage milestone). Have humans approve tone and factual claims to keep authenticity.
13.2 User-generated content and social proof automation
Automate collection of testimonials and ratings post-purchase (quick one-question surveys with incentive). Feed verified snippets into ChatGPT-5 to create micro-testimonials tailored per segment (“customers like you in [city] say…”). Rotate social proof to avoid repetition and always be transparent (e.g., “Rated 4.8/5 by 12,432 customers”).
13.3 Product recommendation engines driven by short prompts
Combine simple rules and LLMs for recommendations: use deterministic signals (past purchases, category affinity) to select candidate products, then ask ChatGPT-5 to craft a short human-friendly blurb for each product tailored to the user’s segment. Keep templates tight (“Because you viewed [category], we think you’ll love — key benefit + CTA”) and A/B test placement and phrasing.
13.4 Win-back sequences with emotional triggers
Design multi-step win-back flows that escalate emotionally and offer increasing value: Step 1 — gentle nudge with a helpful tip; Step 2 — highlight what’s new or changed since they left; Step 3 — limited-time incentive + social proof; Step 4 — final “we’ll miss you” message with an easy re-opt option. Use storytelling and empathy (recognize possible reasons for inactivity) rather than guilt or pressure.
14. Templates, Playbooks & Reusable Assets
Turn successful experiments into assets so wins compound over time.
14.1 Ready-to-use prompt templates for subject lines, bodies, previews
Maintain a library of standardized prompts with placeholders, e.g.:
“Act as a conversion copywriter. Audience: {segment}. Product: {product_name}. Goal: {goal}. Produce 8 subject lines (≤45 chars), 3 preview texts, and 2 body variants (≤90 words). Tone: {tone}.”
Version these prompts and rate their performance so teams reuse the best-performing scaffolds.
14.2 Reusable email templates (welcome, promo, cart, churn)
Store modular HTML templates with named content slots (hero_heading, product_snippet, testimonials_block) so marketing can swap content atoms without dev work. Include tested accessibility and mobile styles and tag templates with last-tested date and approval status.
14.3 Playbooks for seasonality and campaign blasts
Create playbooks that capture timing, cadence, creative themes, discounting rules, and reporting expectations for seasonal campaigns. Include escalation paths for inventory or fulfillment issues and a checklist for legal/partner approvals.
14.4 Content calendar and asset management checklist
Maintain a calendar with campaign owners, deadlines, localization status, asset links, and QA sign-offs. Checklist items for each campaign: copy draft, creative, alt text, links verified, UTMs set, deliverability check, and legal review complete.
15. Human + AI Workflow (Governance & QA)
Scaling AI without governance invites risk. Clear roles and a tight QA loop keep speed and safety aligned.
15.1 Roles and responsibilities: marketer, editor, legal, AI operator
Define who does what:
- Marketer: defines goals, audience, and brief.
- AI Operator: runs prompts, curates outputs, and manages the prompt library.
- Editor: polishes language, checks brand voice, and ensures copy clarity.
- Legal/Compliance: validates claims, required disclosures, and privacy language.
Make approvals explicit — e.g., campaigns with offers or claims require legal sign-off before send.
15.2 Review checklist: accuracy, brand voice, compliance, links
A short, mandatory checklist for every send:
- Factual accuracy and no hallucinated claims.
- Brand voice and tone match.
- Links and UTMs correct and landing pages live.
- Accessibility checks (alt text, hierarchy).
- Opt-out and footer language present.
- No PII in prompts or generated text. Checkboxes + approver initials make this auditable.
15.3 Version control and rollback procedures
Store prompt and template versions in a repository (Git or CMS with versioning). Tag releases used in campaigns and keep quick rollback procedures: disable flow, revert to prior template, and re-send if appropriate. Maintain a changelog so you can trace what prompt or template change coincided with any performance or compliance issue.
15.4 Training teams to write effective prompts and evaluate outputs
Short, practical training accelerates adoption: run workshops with examples of good vs. bad prompts, show how to read outputs critically, and create a scoring rubric (clarity, brand fit, factual accuracy, testability). Encourage a culture of prompt experiments and capture learnings in the prompt library so the whole team benefits.
16. Tools & Ecosystem
Picking the right tools makes LLM-driven email practical instead of painful. You want an ecosystem that supports automation, secure model access, observability, and easy integrations — not a Frankenstein stack you can’t manage.
16.1 Recommended ESP and CRM features to support LLM workflows
Choose an ESP that offers programmatic API access, dynamic content blocks, robust template versioning, and a sane testing workflow (preview, spam checks, and staged sends). Your CRM should support event streaming (real-time behavioral events), flexible custom fields, and user-level consent flags. Critical features: template variables that map directly to CRM fields, an approvals/review queue, and transactional vs. promotional sending separation. If your ESP has a built-in workflow/orchestration engine, verify it supports webhooks or custom actions so you can plug in generated content from ChatGPT-5 safely.
16.2 Handy integrations (Zapier, Workato, webhooks, CDPs)
Integrations glue LLM outputs to your delivery pipeline. Use lightweight automation tools (Zapier, Make) for quick proofs-of-concept and enterprise-grade platforms (Workato, Mulesoft) for production flows. Webhooks are essential for event-driven generation (e.g., create drafts when a cart-abandon event fires). A CDP (customer data platform) that unifies identity, segments, and events simplifies prompt inputs and ensures your model sees consistent, non-PII context. Prefer direct API connections for production-critical paths to avoid latency and reliability issues.
16.3 Monitoring and observability tools for campaigns
Observability should cover both technical health and performance outcomes. Use email-specific tools for inbox placement and rendering tests, a monitoring stack (Datadog, Grafana) for API latency and error rates, and analytics dashboards (Looker, Data Studio) for funnel metrics. Implement synthetic tests: render previews, validate links, and run a smoke test send to a seed list before wide release. Instrument LLM usage (requests, tokens, latency, errors) and correlate those signals with campaign KPIs to spot systemic problems early.
16.4 Cost considerations and API usage optimization tactics
LLM usage costs can scale quickly if you treat the model like a single-source for every word. Optimize by: caching common outputs (subject lines, snippets), using smaller models for low-risk tasks (paraphrasing, simple templates), batching prompts where possible, and setting strict token limits. Track token usage per campaign and tag prompts with cost-center metadata so finance can monitor spend. Also consider hybrid strategies — use ChatGPT-5 for ideation and a lighter local NLU for deterministic rendering — to reduce expensive round trips.
17. Scaling & Organizational Adoption
Scaling AI in email isn’t just technical — it’s organizational. Successful adoption balances quick wins with long-term governance.
17.1 From pilot to enterprise: roadmap and success milestones
Run a tight pilot: pick one high-impact journey (welcome or cart recovery), measure baseline performance, deploy LLM-assisted variants, and evaluate lift. Milestones: pilot completion (data quality validated), repeatable prompt templates (50% reduction in draft time), and measurable ROI (X% lift in CVR). Move to “productize” stage with hardened templates, permissions, and audit logs before enterprise rollout. Each stage should have clear exit criteria to avoid scope creep.
17.2 Governance, security, and procurement checklist
Enterprise adoption needs procurement buy-in and security assurances. Checklist items: vendor security posture, data residency and processing terms, access controls for APIs, role-based prompt permissions, and incident response plans. Add procurement items like SLAs, support tiers, and integration costs into the total cost-of-ownership evaluation.
17.3 Cross-functional buy-in: sales, product, customer success alignment
Email intersects many teams. Bring stakeholders together early with concrete demos and metrics they’ll care about (lead velocity for sales, retention for customer success, activation rates for product). Create shared KPIs and run joint experiments so wins are credited cross-functionally. Build a “marketing-operational” forum that meets regularly to review tests, prioritize requests, and coordinate content localization or legal reviews.
17.4 KPIs to justify expansion and budget allocation
Track direct and indirect ROI: incremental revenue per campaign, speed-to-publish (reduction in time to create drafts), reduction in agency or freelance costs, and uplift in retention or activation. Present both leading indicators (CTR lift, engagement lift) and lagging financial metrics (incremental revenue, cost per acquisition improvement) to stakeholders when asking for budget to scale.
18. Advanced Topics & Future-Proofing
Plan not just for today’s tactics but for the capabilities coming over the next 12–36 months. That keeps your program resilient and competitive.
18.1 Multimodal content (images, audio snippets) alongside email copy
Emails are evolving to include rich, personalized media. Use LLMs to produce image captions, audio script summaries, or personalized subject images (via programmatic image APIs). Keep media filesize and deliverability in mind: favor hosted media and preview-friendly formats, and always supply textual fallbacks for accessibility and clients that block media.
18.2 Adaptive campaigns that learn from continuous feedback loops
Build feedback loops where performance data updates segment definitions and prompt templates automatically. For instance, a model can surface top-performing opening lines each week; a pipeline validates them and promotes winners into the template library. This continuous learning shortens the experiment cycle and embeds signal-driven optimization into day-to-day operations.
18.3 Ethical considerations and bias mitigation in LLM outputs
LLMs can inadvertently perpetuate bias or harmful phrasing. Mitigation requires prompts that ban discriminatory language, human review for sensitive segments, and periodic audits of outputs across demographics. Document decision rules for personalization that could create unfair outcomes (e.g., offering different discount levels by protected attributes) and ensure compliance with local laws and company ethics standards.
18.4 Preparing for new channels (SMS, in-app, social DMs) with shared prompts
Repurpose successful email prompts for other channels by adding channel constraints (character limits, tone, interactivity). Maintain a single source of truth for campaign intent and assets so messages across email, SMS, and in-app maintain consistent promises and timing. Centralized prompts with channel-specific adapters speed omnichannel campaigns and preserve voice.
19. Step-by-Step Implementation Checklist (90-day plan)
A pragmatic timeline turns strategy into action. Below is a focused 90-day plan to go from zero to repeatable LLM-driven email campaigns.
19.1 Week 1–2: Data & infrastructure setup
- Audit existing data fields and consent records.
- Identify and fix critical gaps (e.g., missing last_purchase_date).
- Configure basic ESP–CRM integrations and test webhooks.
- Establish prompt governance rules and a secure testing environment.
19.2 Week 3–6: Pilot campaigns and A/B tests
- Select one pilot journey (welcome or cart recovery).
- Create prompt templates and generate draft variants.
- Run human QA and send to a seed cohort.
- Execute A/B tests on subject lines and CTAs; collect baseline metrics.
19.3 Week 7–12: Scale, monitor, and optimize
- Promote winning variants into production templates.
- Automate generation for similar segments and add localization.
- Monitor deliverability and API health; iterate on prompts to reduce token usage.
- Document learnings, update playbooks, and prepare governance checklists for expansion.
19.4 Quick wins and long-term initiatives to prioritize
Quick wins: subject-line banks, dynamic snippets for top product categories, and a re-engagement flow. Long-term initiatives: building a CDP-backed identity layer, integrating enterprise LLMs with VPC/enterprise controls, and training programs to upskill teams.
20. Case Studies & Benchmarks
Real examples make the abstract concrete. Here are archetypal case studies and the lessons they teach.
20.1 Example: Welcome series that doubled activation (what changed)
Hypothesis: personalization + clear next step increases activation. Change: replaced generic welcome with three hyper-personalized emails generated from signup data (product interest, recommended first actions, and social proof). Result: activation rate doubled within 30 days. Lesson: small, behaviorally-triggered nudges with explicit CTAs beat long, generic onboarding sequences.
20.2 Example: Cart recovery sequence improvements (metrics before/after)
Change: introduced a 3-step sequence using urgency (hourly), social proof (review snippet), and a small discount. ChatGPT-5 generated tailored product descriptions per user. Result: conversion rate improved 20% and average order value rose by 8% due to bundled recommendations. Lesson: combining behavioral timing with tailored messaging improves both conversion and basket size.
20.3 Benchmarks by industry and list size
Benchmarks vary widely; small, highly engaged lists often outperform large, purchased lists. For healthy in-house e-commerce lists, expect CTRs in the mid-single digits and CVRs of 2–5% depending on offer and audience. B2B tends to see lower open rates but higher LTV per conversion. Use your own pilot as the primary benchmark — industry averages only guide hypotheses.
20.4 Lessons learned and repeatable best practices
- Start small and measure everything.
- Keep humans in the loop for review and ethical guardrails.
- Standardize prompts and version them like code.
- Prioritize data hygiene — the best prompt can’t save bad data.
- Invest in observability so you can link LLM usage to real business outcomes.
Summary
This guide walked through a complete path for building high-conversion email campaigns with ChatGPT-5: start with a clear strategy and measurable goals, collect and clean the right data, design prompts and templates that produce consistent outputs, and embed human governance for quality and compliance. From creation to delivery — and through continuous testing and observability — the goal is to make email more relevant, scalable, and accountable. Think: Strategy → Data → Creation → Delivery → Optimization → Scale.
Final checklist — must-do items before sending your first ChatGPT-5 powered campaign
- Define the campaign goal and primary KPI (CTR, CVR, revenue per recipient).
- Confirm segmentation is mutually exclusive and your cohort sizes meet test-power needs.
- Validate data fields used in prompts (no raw PII in prompts).
- Ensure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are configured for your sending domain.
- Run template rendering tests across major clients and mobile sizes.
- Generate at least 8 subject-line variants and 3 preview texts; select via A/B testing plan.
- Populate and test all UTMs and event-tracking hooks.
- Perform legal and compliance review of offers, footer, and opt-out language.
- Queue drafts into a human approval workflow and complete the review checklist.
- Run a seed send to internal inboxes and monitor deliverability/engagement for 24–48 hours.
Encouragement
You don’t need to perfect every prompt or automate every email to get value from ChatGPT-5. Start with one high-impact journey, measure the lift, keep humans in the loop, and iterate. Speed without discipline wastes tokens; discipline without experimentation stalls growth. Combine both, and you’ll get faster wins that scale into meaningful business outcomes. If you want, I can now build the prompt library, a ready-to-use welcome series, or the downloadable 90-day implementation checklist — tell me which and I’ll make it.